Rhythms in Notation
In most music, rhythmic durations are measured and timed within the framework of a steady beat. To put it another way, rhythms are created by subdividing the beat into shorter durations or by adding them together into longer durations. All rhythmic values (durations) of notes and rests can be defined by their relationships to each other, as in the table below. In order to understand rhythms, we must first understand these relationships.
Relative Durations
In music notation, rhythms are indicated with variations in the way notes are shaped on the page. The durations are relative: a whole note is equal to the duration of two half notes, four quarter notes, eight eighth notes, and sixteen sixteenth notes.
| Whole Note: | ||||||||||||||||
| Half Notes: | ||||||||||||||||
| Quarter Notes: | ||||||||||||||||
| Eighth Notes: | ||||||||||||||||
| Sixteenth Notes: | ||||||||||||||||
Each duration of note has a corresponding rest of the same length. Whole and half rests look almost the same, but a whole rest hangs below the center staff line, and a half rest sits on top of it.
 =
= 
 =
= 
 =
= 
 =
= 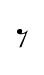
 =
= 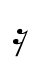
| Whole Rest: | ||||||||||||||||
| Half Rests: | ||||||||||||||||
| Quarter Rests: | ||||||||||||||||
| Eighth Rests: | ||||||||||||||||
| Sixteenth Rests: | ||||||||||||||||
Beams and Flags
The flags on eighth notes and sixteenth notes can be joined together into beams. This helps to keep fast rhythms from looking cluttered.

Dotted Rhythms
Adding a dot to the right of the note head makes the note duration one and a half times (150%) of the starting value. For example, a dotted half note is equal to the duration of a half note plus a quarter note (a half note tied to a quarter note).
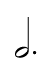 =
= 
Adding a dot to a rest makes the rest one and a half times (150%) of its original duration, just as it does with notes.
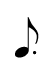 =
=
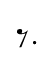 =
= 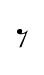
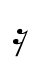
Triplets
Triplets are indicated by placing a 3 (and sometimes a bracket) over or under a group of notes. The duration of three eighth-note triplets is equal to the duration of two standard eighth notes, or one quarter note. To put it another way, while eighth notes divide a quarter note into two parts, an eighth-note triplet divides a quarter note into three parts.
 =
=  =
= 
As another example, the duration of three quarter-note triplets is equal to the duration of two standard quarter notes, or one half note. Quarter notes divide a half note into two parts, while quarter-note triplets divide a half note into three parts.
 =
=  =
= 
Rests can also be triplets just like notes. It is even common to see rests and notes within a group of triplets.
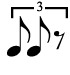
Listen to the relative durations of notes here:

